What is Folliculitis
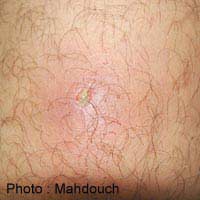
If you are experiencing hair loss in combination with itching or soreness in the affected area, you may have folliculitis. This is often a temporary condition but severe cases can be ongoing and cause lasting damage. It can develop anywhere on the body. How can you tell if your problem is caused by folliculitis, and what can you do about it?
Identifying Folliculitis
Folliculitis occurs when the follicles from which hair grows become infected. This leads to swelling and thus to discomfort; it can also force out the growing hair at the root. Untreated folliculitis sometimes causes scarring, permanently destroying the follicles.If you suspect folliculitis, examine the base of your hairs to see if there are white or red swollen patches. When gently pressed, these will often exude pus or blood. There are, however, a few other medical conditions that can cause similar symptoms, so if the problem persists despite treatment, consult your GP.
After they have been broken, folliculitis-damaged hair follicles often form scabs. Be careful not to pick at these as this can make the problem worse. If you develop a fever or the affected area feels warm, Contact Your GP to ask for advice.
In most cases, folliculitis goes away by itself within a couple of weeks. Young children, elderly people and people with impaired immune systems may find that it takes longer. Acting quickly to treat the problem will reduce the prospect of long-term damage.
Causes of Folliculitis
Folliculitis can be caused by fungal, bacterial or, rarely, viral infections. It is more likely to occur if the follicles are already damaged, for instance, from scratching or from clogging with sweat. Careful hair care using the right shampoo and conditioner for your hair type can help to reduce the problem.Occasionally, a similar condition can occur as a result of ingrowing hair. This is most common where the hair is frequently shaved and the best solution is usually to let the hair grow. In rare cases, folliculitis occurs because hair follicles try to produce multiple hairs, which they cannot support. This form of folliculitis is sadly untreatable.
People with chronic underlying conditions, such as diabetes or HIV, and people who are receiving immunosuppressive treatment for illnesses like cancer or rheumatoid arthritis, are at an increased risk of developing folliculitis. If you are in one of these groups, you should pay more attention to possible symptoms.
Prevention is Better than Cure
There are several ways you can alter your lifestyle so that you are less likely to develop folliculitis. The most important step you can take is to protect your immune system and skin. Don't take antibiotics unless your doctor assures you they're really necessary. Don't use swimming pools or jacuzzis that haven't been properly treated with chlorine, and dry yourself immediately after emerging from shared pools or baths.Washing hair regularly is important, as is protecting your follicles from clogging agents. Avoid wearing cosmetics close to your hairline. If you work in an oily or heavily polluted environment, keep your hair covered. The risk of folliculitis on the body can be reduced by avoiding wearing tight clothing or clothing that doesn't let skin breathe.
Treating Folliculitis
Mild folliculitis can be treated at home using special medicated shampoos (ask your pharmacist), or by gently rubbing the affected area with an astringent such as white wine vinegar or lemon juice – this will draw out moisture and so reduce swelling.If your folliculitis does not go away with home treatment, or if it causes severe problems, you should seek medical help. Most serious cases of folliculitis can be treated effectively with antibiotics or with an antiseptic or antifungal cream (once the exact cause has been diagnosed). If you suffer from recurring folliculitis, you should be referred to a dermatologist for specialist treatment.
It is important not to use hair loss treatment products like rogaine or finasteride if you believe you may have folliculitis. This is because they may get directly into the bloodstream and cause health problems.
Healthy Hair
Using the right shampoos and conditioners for your hair type and adhering to simple styling techniques can help to keep your hair in the best condition. Find out more in our General Hair Care article.- Can Hair Care Products Cause Hair Loss?
- Poisoning and Hair Loss
- What Is Kerion Celsi?
- Piedra and Hair Loss
- Ringworm and Hair Loss
- Radiation and Hair Loss
- Understanding Hypotrichosis Simplex
- Diabetes and Hair Loss
- Alcohol and Hair Loss
- Hair Dye Allergies and Hair Loss
- Seasonal Hair Loss
- Anaemia and Hair Loss
- Body Building and Hair Loss
- Can Surgery Cause Hair Loss?
- Genes and Hair Loss
- Lupus and Hair Loss
- Dreadlocks and Hair Loss
- Scalp Damage and Hair Loss
- Infant Hair Loss
- Pollution and Hair Loss
- Sikh Men and Hair Loss
- Medication That Causes Hair Loss
- Can Hair Loss be a Sign of Other Ailments?
- Causes of Losing Body Hair
- Hair Loss Linked to Tooth Infections
- Hair Loss and Smoking
- What Causes Male Pattern Baldness?
- Stress and Hair Loss
- Types of Alopecia
- What Causes Alopecia?
- What is Alopecia?
- Hereditary Hair Loss
- Causes of Temporary Hair Loss
- Diet and Hair Loss
- What is Trichotillomania?
- Cancer and Hair Loss
- Ageing and Hair Loss
- What is Male Pattern Baldness?

Re: Can Head Lice and Parasites Cause Hair Loss?
I got parasites from a person that stayed in my house. I had to go to the ER 2 times to get this 1 pill . I…
Re: Hair Loss Linked to Tooth Infections
I had a root canal and a crown on upper left and a crown on upper right. Shortly afterwards ( about 3 weeks) my hair…
Re: Wigs and Allergies
I’ve been a hair club client for over 15 years without any issues. Hair club says they use real hair and glue and tape are used to secure hair…
Re: One-sided Hair Loss
Im a 29 year old woman and also have less hair on the right side of my head, It has been like this for years, that side also grows slower than…
Re: Hair Integration Pieces
Hi. I am desperately trying to find a intergrated mesh hair system that can be attached with either tapes or micro links that my…
Re: Starting to Wear a Wig
Due to rapid hair loss I am thinking of getting a wig ,what type would people recommend,thank you
Re: Starting to Wear a Wig
I am rapidly losing my hair and am thinking about getting a wig ,what sort would eolee recommend please .
Re: Poisoning and Hair Loss
Happend to drink an 6 mounth old, not opend nutrition drink.. I don´t know if thats what cause my hair loss. The hair loss is in one…
Re: Can Head Lice and Parasites Cause Hair Loss?
I keep seeing little brown bugs crawling up my shirt and I can’t stand it! My parents keep telling me it’s…
Re: How Often Should You Wash Your Wig?
My wig gets rubbedd by coat collars etc and is getting to feel (and look like)a brillo pad on the bottom of shouder…